Energy-Saving Copper Tube Aluminum Fin Water to Air Heat Exchanger
- Model
- BY-ZFQ
Item specifics
- Core Component
- Finned tube heat exchangers
- Tube Diameter
- 7mm, 9.52mm, 12.7mm, 15.88mm
- Casing Material
- Galvanized Steel, Aluminium, Stainless Steel
- Tube Material
- copper, stainless steel
- Fin Material
- aluminum, copper, stainless steel
Review
Description
Definition:
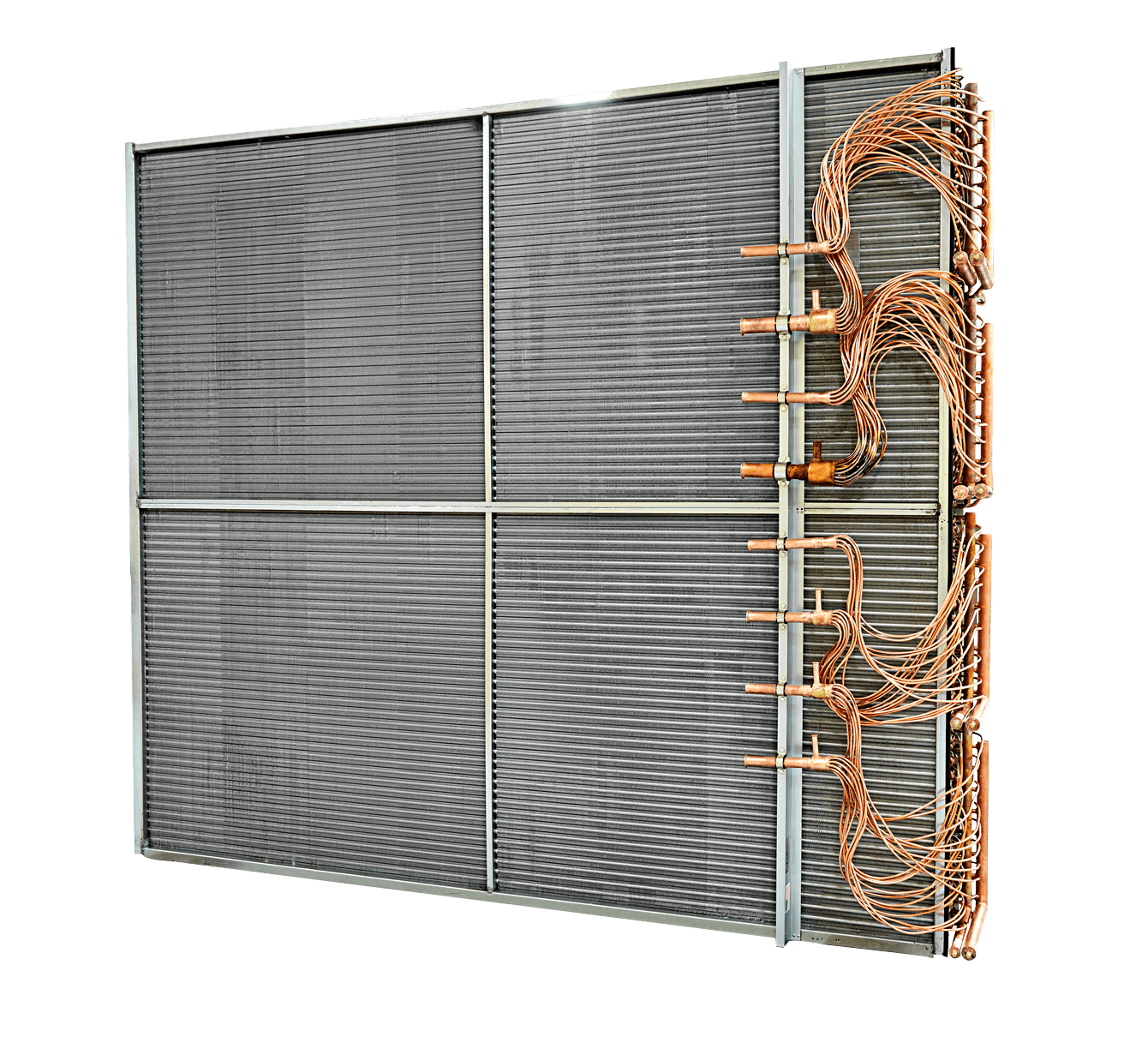
Evaporator coils are used to absorb heat in air-conditioning or refrigeration systems. They facilitate a crucial step in the refrigeration cycle by allowing low-temperature, low-pressure liquid refrigerants to evaporate into gas, thereby absorbing heat from the surrounding environment. Evaporator coils are one of the four main components in the refrigeration or air-conditioning cycle. Whether in commercial central air-conditioning systems or precise industrial cooling equipment, evaporator coils provide efficient cooling. Especially in environments requiring strict control of humidity and air quality, the role of evaporator coils is particularly prominent.
How They Work:
1. Refrigerant Flow: Low-pressure liquid refrigerant enters the coil via an expansion valve, which regulates the flow.
2. Heat Absorption: As warm air passes over the coils, the refrigerant absorbs heat, causing it to evaporate into a gas.
3. Cool Air Circulation: The now-cooled air is blown into the living space (in ACs) or cools the refrigerator compartment.
4. Cycle Continuation: The gaseous refrigerant travels to the compressor to restart the cycle.

Construction & Materials:
1. Metals Used: Typically copper (for tubing) and aluminum (for fins) due to their excellent thermal conductivity.
2. Design Features: Fins increase surface area for efficient heat exchange. Coil shapes vary (e.g., A-shaped in ACs, flat in fridges).
Types of Evaporator Coils:
1. A-Coils: Common in residential ACs, shaped like an "A" for optimal airflow.
2. Slab Coils: Flat designs used in refrigerators and freezers.
3. Multi-Circuit Coils: Found in commercial systems for handling larger loads.
Applications:
1. Residential: AC units, refrigerators.
2. Commercial: Walk-in coolers, supermarket display cases.
3. Industrial: Large-scale refrigeration, chemical processing.
4. Heat Pumps: Act as evaporators in cooling mode and reverse to condensers in heating mode.
Maintenance & Common Issues:
1. Dirt/Dust Buildup: Reduces efficiency; clean coils annually with a soft brush or coil cleaner.
2. Ice Formation: Caused by low refrigerant, poor airflow, or faulty components. Address promptly to prevent damage.
3. Refrigerant Leaks: Lead to poor cooling; require professional repair.
4. Bent Fins: Restrict airflow; gently straighten with a fin comb.
Our mission:
Choose our heat exchangers for efficient and reliable cooling solutions. Experience the benefits of our advanced technology and enjoy peace of mind knowing your equipment and environment are protected.
Our mission is to research and develop high-efficiency freezing equipments unceasingly, committing to better serve the product application market.
- Specifications can be tailored to suit each application, with different materials, sizes, noises and cooling mediums available.
- contact us







