A brief discussion on "wet curtain (cooling pad)"
- Share
- publisher
- Sam Chang
- Issue Time
- May 19,2025
Summary
Wet curtain (water curtain) cooling primarily utilizes the physical principle of water absorbing heat from the air during the evaporation process, thereby lowering the air temperature.
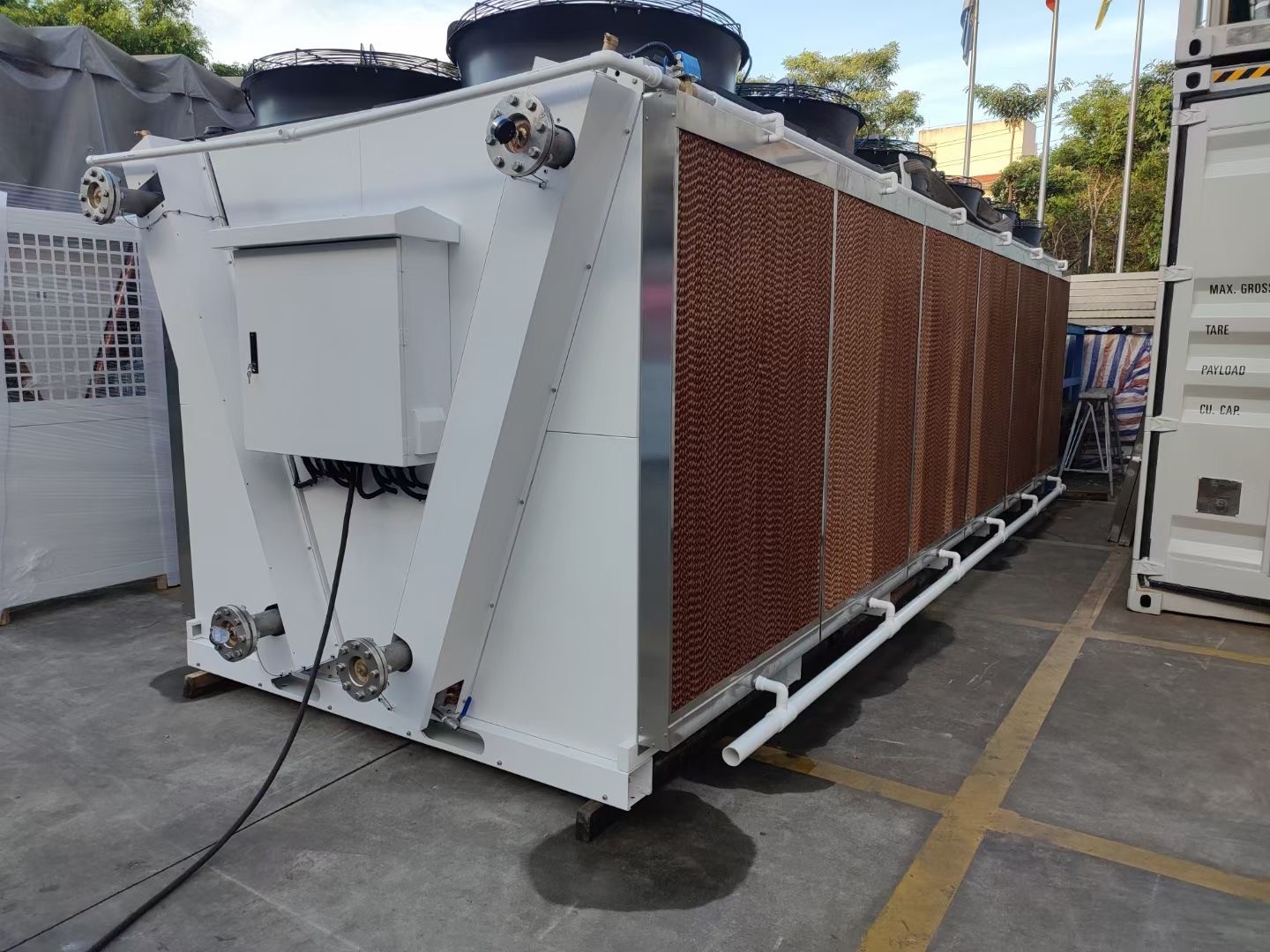

A brief discussion on "wet curtain (cooling pad)"
In practical applications, when used in conjunction with negative pressure fans, the wet curtains are installed on one end gable or side wall of an enclosed room, while the fans are mounted on the opposite end gable or side wall. The cooling fans extract indoor air, creating negative pressure that forces outdoor air to flow through the porous, moistened surface of the wet curtains. This process facilitates the transfer and dissipation of a significant amount of heat from the air, thereby reducing the temperature of the incoming air by 4-10°C. The cooled air is then continuously introduced into the room for heat relief and cooling purposes.
What are the thicknesses of the water curtains?
The thickness of cooling pads mainly comes in three types: 10 cm, 15 cm, and 20 cm, with 15 cm being the most widely used. The diameter of the honeycomb holes in cooling pads primarily includes 5 mm, 7 mm, and 9 mm, with 7 mm being the most common. The 5 mm type is used for environmental air conditioners (cooling fans), while the 9 mm type is suitable for dusty environments prone to clogging. Based on the corrugation angle, they can be categorized into 45°+45°, 30°+60°, and 45°+15°.
What are the models of water curtains?
The models of cooling pads are 5090, 5060, 7090, 7060, 9090, and 9060. The commonly used models for cooling pads are 7090 and 7060, but other models can also be customized based on different requirements.
What are the categories of wet curtains?
The main types commonly available include: 7090-type wet pads, 7060-type wet pads, and nowadays, some customers opt for these yellow-and-green alternating wet pads, also called green-striped wet pads, for a more aesthetically pleasing appearance. Additionally, there is another type with a black coating on the surface. Basically, these are the four common types of wet pads. Of course, 7090 and 7060 are the two types most frequently used in agriculture. In industrial applications, there is also the 5090-type wet pads.
What are 7090 and 7060?
The terms 7090 and 7060 refer to the height of the corrugation peaks and valleys, where "70" means 7 millimeters. "90" indicates that the angle formed during the production and bonding process of the cooling pad is 90 degrees. A 90-degree cooling pad is created by bonding two 45-degree cooling pad sheets together. A 60-type cooling pad, on the other hand, is made by bonding a 45-degree cooling pad sheet with a 15-degree sheet, resulting in the final product.
Additionally, the green-striped cooling pads are essentially the same as the common 7090 and 7060 types, but with a color variation for enhanced aesthetics.
However, the black-coated surface of the wet pad we are discussing carries a deeper significance, which is mainly reflected in the following aspects: First, it prevents algae growth, a function of considerable importance. Additionally, it enhances the surface strength of the wet pad, thereby extending its service life.
What are the evaluation indicators for wet curtains?
Whether it's the 7060-type or 7090-type wet curtain, what we truly focus on is the performance of the wet curtain paper. To evaluate it, we primarily consider several key indicators: the first is the wet curtain's wet strength, and the second is its water absorption—these two metrics are absolutely critical. Wet strength essentially refers to the durability of the wet curtain, a challenge that has now been largely resolved by manufacturers in the industry. In the past, some wet curtains lacked sufficient wet strength, leading to issues like collapsing during use or shrinking after water exposure. However, this problem has now been effectively addressed by our manufacturers.
Another important indicator is the water absorption rate of the cooling pad. How is the water absorption rate calculated? Essentially, it involves measuring the dry weight of the cooling pad, then soaking it in water. After letting it drain for three minutes, we measure its wet weight. The water absorption amount is obtained by subtracting the dry weight of the cooling pad from its wet weight. The water absorption rate is then calculated by dividing the water absorption amount by the dry weight of the cooling pad and multiplying by 100%. In practice, the water absorption rate of the cooling pad is a crucial metric during its use.
What is the difference between the 7060 type wet curtain and the 7090 type wet curtain?
Actually, the differences between the 7060 and 7090 mainly manifest in three aspects. The first is what we call the humidification efficiency of the wet pad. The 7060-type wet pad and the 7090-type wet pad have different humidification efficiencies, and this difference leads to our second point—the cooling effect. This is a topic of greater concern during practical use, specifically how effective the wet pad is at cooling in real-world applications. Additionally, under the same wind speed conditions, the 7060-type wet pad and the 7090-type wet pad will generate different levels of negative pressure on the fan's negative pressure system.
Now let’s take a look at the tables showing the humidification efficiency and pressure drop for the 7060-type wet pad and the 7090-type wet pad. From these two tables, we can observe the curves of humidification efficiency and pressure drop for the 7060-type and 7090-type wet pads under different wind speeds. For example, when we take an air velocity of 2 meters per second through the wet pad, we can see the humidification efficiency of the 7090-type wet pad. Basically, for a 15CM wet pad paper, as shown in the lower curve, its humidification efficiency is approximately 85%. At the same time, the pressure drop it generates at 2 meters per second is around 40 Pascals.
Additionally, let's look at the 7060-type wet curtain. With a face velocity of two meters per second, the humidification efficiency of the 7060-type wet curtain is approximately 74%.
At the same time, its pressure drop will also be slightly lower, around 20 Pa. This reflects the difference in humidification efficiency and pressure drop between the 7060 type and the 7090 type wet curtains under the same wind speed conditions.
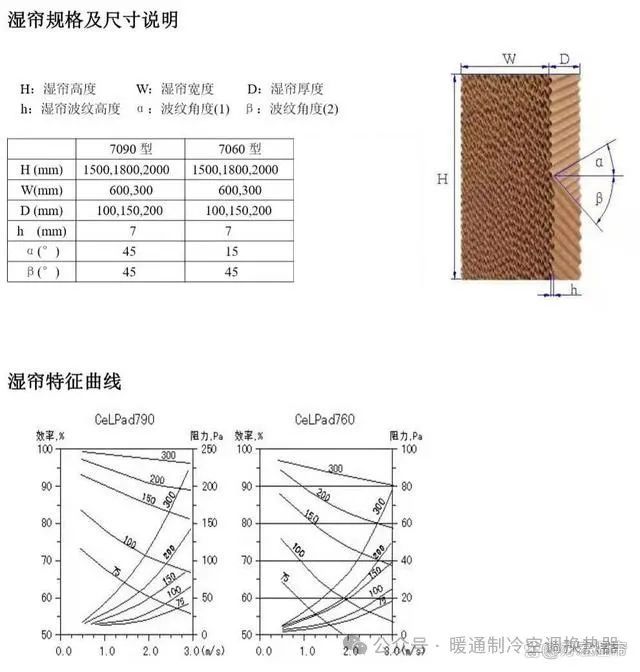
Wet curtain specifications and size descriptions:
This result serves as a reference for us when designing wet curtains and environmental control systems, especially in determining the appropriate negative pressure for our ventilation systems. Because when designing ventilation, the system will not operate under 0 Pa conditions. We always need to calculate, for example, where pressure losses may occur in the system.
For example, a wet curtain may cause a pressure loss of 20 Pa or 30 Pa. The question is how much pressure loss will be generated inside a pig house. After adding these values together, we can evaluate whether to adopt a design value of, say, 30 Pa for our fan. Of course, the air volume at 30 Pa is different from that at 0 Pa.
Therefore, the pressure drop loss caused by the wet curtain is an important reference indicator for us. Of course, we also consider the cooling effect of the wet curtain—the actual cooling performance—when selecting different air velocities. Below, I’ve listed two air velocities as references for the design of the 7090-type wet curtain and the 7060-type wet curtain.
For the 7090 type wet curtain, we generally recommend a wind speed of 1.5 to 2 meters per second. As for the 7060 type wet curtain, because of its lower wind resistance and reduced pressure drop, we can adopt a slightly higher wind speed, such as 2 to 2.5 meters per second, when designing the wet curtain.